Passive Design
Designing the building and the spaces within it to benefit from natural light, ventilation and even temperatures.
Shading
Shading should be designed to take into account the sun's path in summer and winter.
In general, midday summer sun is not difficult to exclude through windows that face within 20° of solar north. The sun’s high angle means that it will not enter these windows during the summer months if shaded by eaves or external shades.
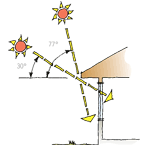
- Midday sun for summer and winter solstice for Auckland
The sun’s altitude angles at midday on the summer and winter solstices are shown for the Auckland area.
It is more difficult to shade east and west faces as they receive low morning and afternoon sun. Where low sun is a problem, keep east and west facing glazing to a minimum.
The following table recommends shading options for different situations.
Orientation | Sun direction | Time of day | Type of shading |
|---|---|---|---|
North | High angle | Middle of day | Fixed or adjustable above window |
East-west | Low angle | Morning/evening | Adjustable screens/shutters |
NE/NW | Low angle | Morning/evening (winter) | Adjustable shading |
To design effective shading, it is important to have a good understanding of sun paths at the site at different times of the year.

