Energy
Designing homes to conserve energy and use it efficiently, from sources that cause least environmental harm.
Fixed wiring for electrical systems and appliances
There is a range of typical and additional wiring requirements for various electrical systems and appliances.
On this page:
- heating systems
- hot water systems
- cooking appliances
- ventilation systems.
Heating systems
| System | Typical wiring requirements | Additional requirements |
| Heat pump | Wire to the condenser (outside unit) with a single-phase, 20 amp supply. | • Larger units may require a 4 mm2/32 amp supply • Ducted or multi-evaporator systems require a three-phase supply. |
| Undertile heating | 1.5 or 2.0 mm2 (depending on wattage) two-core plus earth dedicated supply circuit. | Requires: • RCD protection • floor sensor • programmable thermostat (located outside the damp area zone). |
| Embedded floor heating | 2.5 or 4.0 mm2 two-core plus earth (depending on wattage) dedicated supply circuit. | Requires: • RCD protection – protection not exceeding 30 mA, except for MIMS (mineral insulated metal sheathed) cables • floor sensor • programmable thermostat • a well-insulated slab (50 mm minimum polystyrene slab insulation) with edge insulation. |
| Heat, extraction and light units | May be wired directly into lighting circuits. | May be timer-controlled for the extraction function. (Note: If wiring the unit to the switches is a problem in a retrofit situation, some models are available with a wireless remote. Some models also have automatic humidity control for the exhaust fan.) |
| Infrared heater in a bathroom | Must be wired into the power point circuit. | May be controlled with: • manual switch • timer. |
| Nightstore heater | May be wired directly into power circuits. | Frequently installed to use the lower cost night rate power, therefore requires separate meter and direct wiring back to distribution board. |
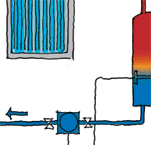
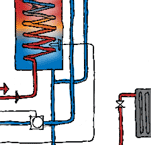
| Solar/wetback/electric water heating | Wired directly from the distribution board or through a programmable solar controller so that power is provided to the element only when there is no solar heating and the water temperature is lower than a preset temperature. | If cylinder has a controlled or separately metered power supply, a separate power supply to the solar controller must be specified. |
Hot water systems
| System | Typical wiring requirements | Additional requirements |
| Electric hot water system with wetback for hot water use and hot water heating (e.g. radiator, embedded floor heating) | Power supplies required to two pumps: • for the wetback/HWC water reticulation (may not be necessary where HWC is directly above the wetback) • to circulate water through the heating. |
A wetback circulating pump must have a thermostat to close pipes when water gets to preset temperature. The water in the cylinder heats first. When the preset temperature is reached, the HWC thermostat closes, allowing the radiator/embedded floor heating pump to operate. If HWC hot water is drawn off, the thermostat opens and the radiator pump stops operating so priority is given to the hot water cylinder. |
| Heat pump hot water storage | 4 mm2 two-core plus earth TPS cable dedicated supply circuit | Can fit an outside unit to supplement an existing electric cylinder – will require a power supply and control cables between the inside cylinder and the outside heat pump. |
| Gas water heater (instantaneous and storage) | Outdoor units require: • weatherproof power outlet adjacent to or below the unit for ignition and thermostatic control • dedicated circuit • RCD. |
Battery back-up units can be specified to maintain supply to the unit if necessary. |
| Electric water heater (instantaneous and storage) | • Minimum 4 mm2 two-core plus earth TPS with an 8–9 kW unit for a shower supply. • Minimum of 6 mm2 two-core plus earth TPS with a 13–21 kW unit for a system such as a holiday home. |
Mains supply may need to be increased to allow for use concurrently with an oven or hob. Alternatively. install current-limiting circuit breaker to protect the mains (although this may lead to system tripping if power use is not managed correctly). |
| Underbench hot water storage | May: • be looped off the kitchen power outlet circuit (depending on existing loads connected) • have dedicated circuit from the distribution board. |
Cooking appliances
| System | Typical wiring requirements | Additional requirements |
| Range/oven | Requires: • minimum 6 mm2 two-core plus earth TPS cable • protection by a 32–40 amp miniature circuit breaker (MCB) in the distribution board. |
A free-standing range must be: • connected to a dedicated power outlet • have an isolating switch – BRANZ recommends the switch is labelled • located within 2 metres of the range and be accessible without reaching across the cooking surface. |
| Gas hob and gas oven | Requires power outlet for the ignition circuit, clocks and fans. | |
| Wall or underbench electric oven | Requires 2.5 mm2 or 4 mm2 two-core plus earth TPS cable. | Units must: • be hard wired • have an isolating switch – BRANZ recommends the switch is labelled • be located within 2 metres of appliance and be accessible without reaching across it. |
| Electric or induction hob | Requires 2.5 mm2 or 4 mm2 two-core plus earth TPS cable for a four-element hob. |
Ventilation systems
| System | Typical wiring requirements | Additional requirements |
| Kitchen and bathroom extracts | Units can be wired into a lighting circuit. | • Rangehoods require an easily accessible isolation switch – BRANZ recommends the switch is labelled. • If a run-on timer to the fan control circuit is at the switch, an additional cable core is required. |
| Heat recovery ventilation systems | Units can generally be connected to a lighting circuit, but it is recommended to install a separate 10 amp circuit from the distribution board to a power outlet installed in the roof space, as most units are designed to be plugged in. | Some models require an alarm-type control cable from the unit to the programmable thermostatic controller. |
| Ducted heat transfer system (to distribute heat within the building envelope) | System may be looped off a lighting circuit if power supply for a fan only is required. | • Use insulated ducting. • Install a thermostat in the heat source room. • Locate the inlet grille within 1 metre of the heat source. • Specify controllable flow outlet grilles. • Locate ceiling outlet grilles 1 metre from the corner furthest from the door to allow heated air to travel across the room. |
| Positive pressure solar roof space ventilation systems | • May be looped off a lighting circuit if power supply for a fan only is required. • Requires 2.5 mm2 two-core plus earth TPS if a heating element is incorporated. |
Some models require alarm-type control cable from unit to the programmable thermostatic controller. |